Are you struggling to understand the simple gear trains? Confused about how gear ratio, spur gears, and intermediate gears work together in a simple gear train?
Well, you’re not alone. Many engineering students find these concepts kinda tricky.
But don’t worry, I’m here to help. I’ll break down the essentials of simple gear trains, making these foundational concepts clear and straightforward.
What is a simple gear train?
A simple gear train is a gear system that consists of two or more gears, connected together. The gears are each placed on a shaft and each shaft only holds one gear – that’s what makes this gear train a simple gear train.
The end goal is to transmit power to the output shaft.
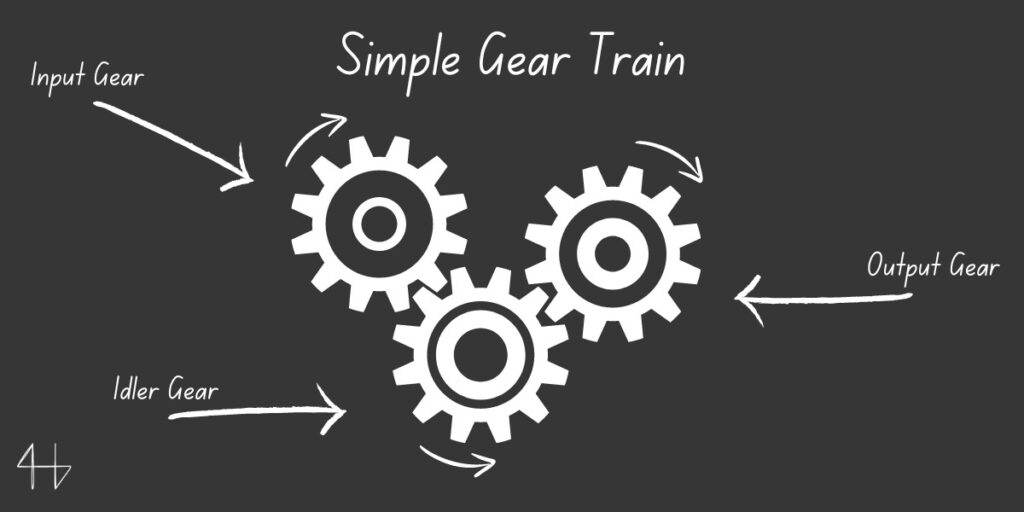
In the example I drew below, the input gear will generally be placed on a shaft that is connected to a motor or some device to generate rotational motion. The Input shaft turns, causing the input gear to turn.
In turn, the input gear turns the idle gear. The idle gear is there just to make sure that the output gear and the input gear rotate in the same direction. (Adjacent gears rotate in opposite directions).
Finally, the idler gear turns the output gear, which is connected to the output shaft.
Input gears are sometimes referred to as driver gears and output gears are referred to as driven gears.
Working principle of a simple gear train
The working principle of a simple gear train is based on the interaction between these gears, primarily focusing on the transfer of rotational motion and torque.
As the driver gear rotates, rotational motion is transferred through the meshing gear teeth pushing on each other. This forces them to rotate around the shat that they are on.
The size of the gears determines the relative speeds and torques of the gears involved.
Advantages vs Disadvantages of Simple Gear Trains
There are advantages and disadvantages to all types of gear trains.
While simple gear trains are relatively straightforward, systems requiring more complex gear arrangements (like compound gear trains) can become intricate and difficult to design and maintain.
Simple gear trains generally consist of fewer components and straightforward meshing arrangements, making them easier for designers, engineers, and maintenance personnel to understand.
This simplicity reduces the likelihood of errors in assembly and maintenance.
Advantages
Disadvantages
Simple gear train applications
Simple gear trains are used in various machines and devices to transmit power efficiently.
By connecting multiple driven gears, these systems achieve the desired speed ratios. This versatility makes them ideal for applications ranging from clocks to industrial machinery, ensuring precise and reliable operation.
Bicycles
In bicycles, the gear system determines speed and ease of pedaling. The number of teeth on the output gear affects this balance.
When the chain moves, the gears rotate in the same direction, ensuring smooth power transfer from the pedals to the wheels.
Conveyor Belts
In conveyor belt systems, idler gears help maintain the overall gear ratio in the simple gear train.
Although it is often designed as a reverted gear train, some use simple gear trains. These gear systems ensure smooth operation and precise speed control, which is crucial for efficient material handling and processing.
Electric Screwdrivers
In electric screwdrivers, an idler gear is often used to maintain the same gear ratio between the driving and driven gears.
This ensures that the gear teeth mesh correctly, providing consistent performance and reliable torque for efficient screwing tasks.
Key Considerations for designing a simple gear train
When designing a simple gear train, it’s crucial to ensure proper alignment of the input gear and meshing gears.
The sizes of the input and output gears determine the overall gear ratio, affecting performance and efficiency. Accurate calculations are essential for optimal operation.
Wrapping Up and My Experience with Simple gear trains
In my experience, understanding the interplay between spur gears and bevel gears is crucial. Mastering these helps achieve the desired combined gear ratio and the right output direction.
Simple gear trains may seem basic, but they are fundamental in various engineering applications. I have personally used simple gear trains when working with French windows and smart hatch hinges.
Project Idea: 3D printed 3-speed ratio gear box






