Ever felt confused trying to figure out what exactly a *miter gear* does or why it’s used? Or how is it different to a bevel gear?
If you’re dealing with machinery or projects that require precise gear systems, getting a handle on miter gears is a great help!
Whether you’re trying to understand *straight tooth miter gears* or *angular miter gears*, grasping the basics can make all the difference. When you factor in things like the *pressure angle*, it can seem a bit overwhelming.
What is a miter gear?
A *miter gear* is a type of gear used to change the direction of motion between two shafts, usually at a 90-degree angle.
You’ll often see them in machines where two parts need to rotate in different directions but at the same speed. Miter gears typically have a 1:1 gear ratio, meaning both gears turn at the same rate.
They come in various types, like ones with spiral teeth, which help reduce noise and increase efficiency at high speeds.
Sometimes, extra work is needed to perfect the gear’s function, known as secondary operations, like polishing or adjusting the teeth. Miter gears are key to a lot of everyday equipment, from car engines to power tools.
Types of Miter gears
There are two main types of miter gears you’ll encounter:
- straight miter gears
- spiral miter gears
Both have the same number of teeth, which means they turn at the same speed, but they differ in how their teeth are shaped.
Straight miter gears have straight teeth, making them simpler to manufacture and more affordable. They’re great for basic applications but tend to get noisy at higher speeds.
Spiral miter gears have curved teeth. These are better for high-performance machines because they run more smoothly and quietly.
But, their design requires more support to handle the extra force they create, and they may need special fittings like a set screw to keep everything in place.
These differences matter in real-world equipment, like cars and power tools, where you need the right gear type for the best performance.
Miter gear working Principle
Miter gears work by connecting two shafts at a 90-degree angle, allowing one to drive the other.
As one gear spins, it transfers motion to the second gear, which moves in the opposite direction at the same speed.
The conical shape of the gears ensures smooth power transfer, making them efficient for machines like drills or engines.
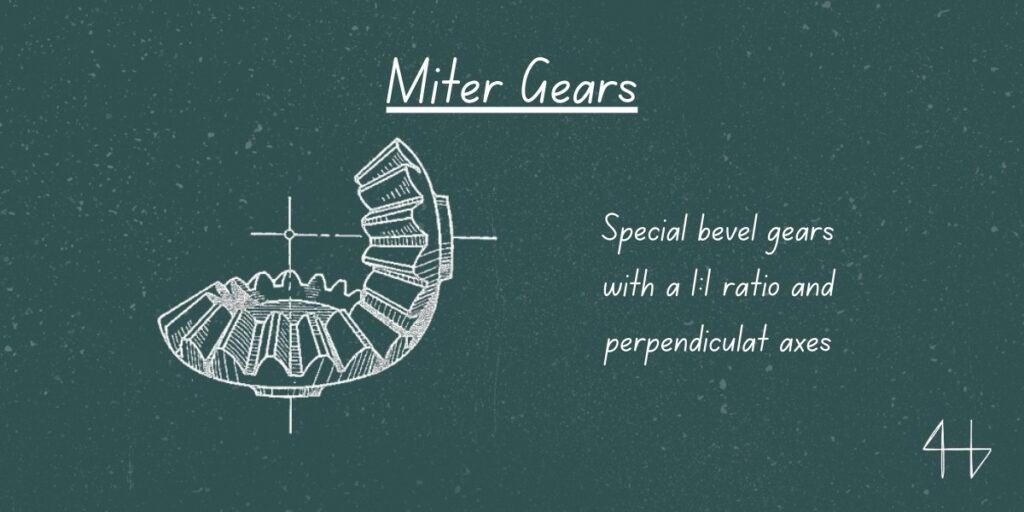
How to Identify miter gears?
You can easily spot a miter gear by its cone-like shape and the way its teeth are arranged. Unlike other gears, miter gears have an equal number of teeth on both gears, creating a symmetrical design.
This is what allows them to change motion direction at a 90-degree angle while maintaining equal speed on both shafts.
Miter gears vs bevel gears
Miter gears are a special type of bevel gears, with equal number of teeth on both gears, so 1:1 gear ratio.
This means they are good at changing direction of rotation between intersecting shafts without affecting speed or torque. Standard bevel gears can have different tooth counts so they can adjust speed and torque, more flexibility in mechanical design.
Miter gears are good for applications where only direction change is needed, other bevel gears are better when variations in mechanical output is required.

When to use miter gear
You should use a miter gear when you need to change the direction of motion between two shafts at a 90-degree angle while keeping their speeds equal.
They’re great for everyday machines like hand drills, where parts need to spin in different directions.
Miter gears are also ideal for smooth, quiet operation, especially with *spiral teeth* for *high-speed* applications.
Manufacturing process of Miter gears
The manufacturing process of miter gears involves cutting gear teeth into a cone-shaped blank using specialised machines.
Common methods include
- Hobbing
- Milling
These methods shape the teeth precisely. After that, secondary operations like heat treatment or polishing may be done to improve durability and performance.
These steps ensure miter gears can handle real-world conditions, like in high-speed tools or car differentials.
Applications of miter gear
Although miter gears may seem quite limited because they always have a 1:1 gear ratio and a 90 degree shaft offset, they can be found in many different applications.
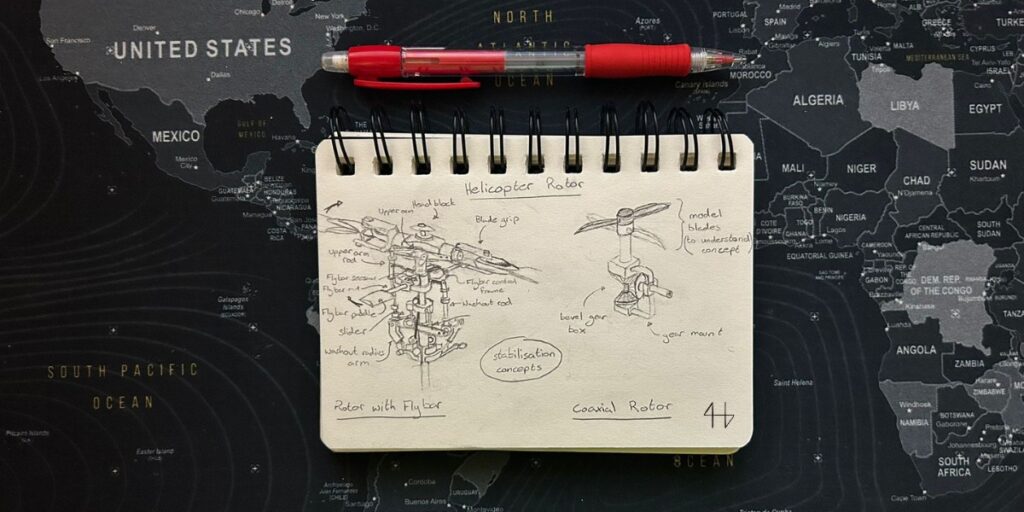
Helicopter rotors
In helicopter rotors, miter gears are part of the power transmission system.
They change the direction of the rotational force from the engine to the rotor blades. This allows the helicopter to achieve the required blade angle and speed for stable flight.
Plus, in some helicopters they are used in coaxial gear boxes, allowing the 2 sets of blades to spin in different directions. This is a stabilization system used in helicopters.
The precision and reliability of bevel gears in this application are critical since they affect the smooth operation and power transmission, directly to the performance and safety of the helicopter.
Robotics
Robotic arms rely on miter gears to achieve precise and controlled movements.
These gears help ensure that the arm can rotate and position objects accurately. This precision is crucial for tasks like assembly, welding, or even delicate handling of materials.
Printing Presses
In printing presses, miter gears control the movement of rollers that press ink onto paper.
They ensure that the rollers rotate properly and consistently, which is essential for producing clear and high-quality prints.
Marine Applications
On boats, miter gears are part of the steering mechanisms and propulsion systems.
They help steer the boat and control the propeller’s direction, making navigation smooth and efficient, whether you’re on a small recreational boat or a large ship.
Industrial Machinery
In industrial settings, miter gears are used in conveyor systems and other equipment to transfer motion effectively.
They help in moving items through production lines or machinery, ensuring that operations run smoothly and efficiently.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Miter Gear
Advantages
Disadvantages
Limitations
Miter gears have a few limitations to keep in mind.
They might not handle heavy loads as well as other gears, making them less ideal for very tough applications. In compact spaces, their need for precise support and alignment can be a challenge.
Also, high-quality miter gears, especially those with spiral teeth, can be pricier to make, which might be a concern for budget-sensitive projects.
Wrapping up
To sum it up, miter gears are crucial in machines that need to change the direction of motion, like in cars or industrial equipment.
Their special design allows them to handle this task efficiently, especially when you need a 90-degree turn. However, be mindful of their limits, such as noise and speed, when choosing them for your project.
FAQs

What are miter gears usually made of?
Miter gears are often made from materials like steel, brass, or plastic.
Steel gears are common in heavy-duty applications because they can handle a lot of stress and wear. Brass gears are used in smaller, less stressful applications and offer good corrosion resistance.
Plastic miter gears are lighter and quieter, making them suitable for devices where noise reduction is important, like in some household appliances.
How do miter gears compare to herringbone gears?
Miter gears and herringbone gears both change the direction of motion but in different ways.
Miter gears have straight or angled teeth that meet at a 90-degree angle, which can create more noise and vibration, especially at high speeds.
Herringbone gears, on the other hand, have teeth that are cut in a V shape, which helps reduce noise and improve smoothness.
This makes herringbone gears a better choice for applications where quiet operation is crucial.
Do miter gears have less backlash than regular bevel gears?
Miter gears generally have more backlash compared to some other bevel gears.
This is because miter gears often have straight or angled teeth that can lead to more play in the gear system.
Regular bevel gears can be designed with various tooth shapes and arrangements that help minimize backlash, resulting in smoother and more precise motion.