Confused about helical gears and why they are different from spur or traditional gears? You’re not alone.
The gear essentials can be complicated at first.
Maybe you’ve noticed your machinery isn’t as smooth or quiet as you’d like or you’re dealing with excessive wear and tear. The problem might be your gear choice.
Helical gears could be the answer you’re looking for, offering benefits over spur gears like reduced noise and smoother operation.
But what exactly makes them different? And how does the helix angle come into play?
What is a Helical Gear?
A helical gear is a gear with teeth cut at an angle, known as the helix angle, instead of straight across like spur gears.
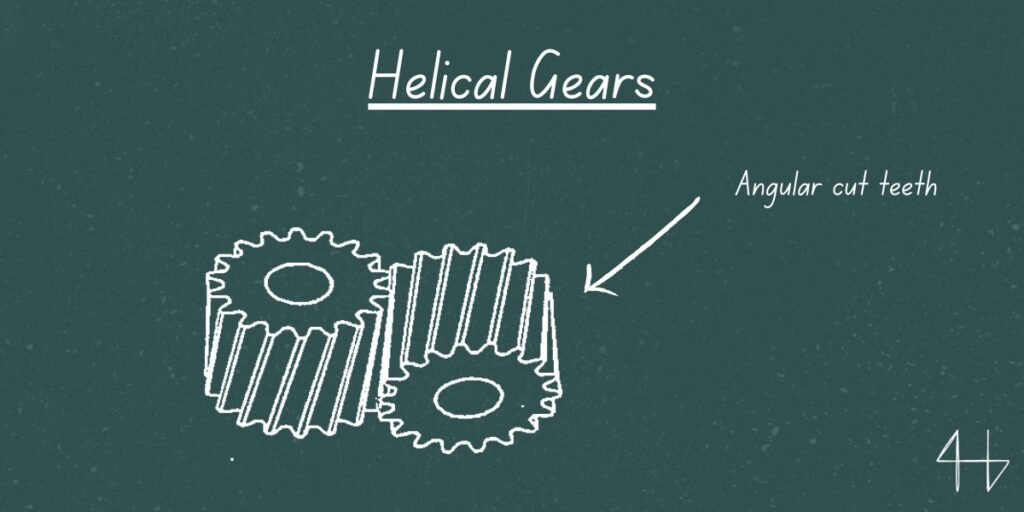
This angled design allows the teeth to engage gradually as the gears rotate, resulting in smoother and quieter operation. Helical gears are used with parallel shafts, where the angled teeth help to distribute the load more evenly across the gear teeth, reducing wear and extending the gear life.
Unlike spur gears which make contact along the entire tooth at once, helical gears engage progressively, minimizing the impact forces and reducing noise.
There are also double helical gears which have two sets of helical teeth, one on each side, cut in opposite directions.
This design cancels out the thrust forces that single helical gears generate, making them ideal for high-power applications where balance is critical.
How to Identify Helical Gear?
Standard helical gears have teeth cut at an angle to the gear’s axis, forming a spiral pattern around the gear.
This is the key feature that sets them apart from spur gears which have straight, perpendicular teeth. When you look at the gear you’ll see the teeth are not straight across but angled in one direction.
If the gear has the angled tooth design on one side only it’s a single helical gear. If you see two sets of teeth cut at opposite angles forming a “V” shape you’re looking at a double helical gear.
Helical Gears vs spur gears
Spur gears have straight-cut teeth that engage all at once, making more noise and vibration.
Helical gears have angled teeth that engage gradually, resulting in quieter and smoother operation.
However, this angled tooth design generates a side force that requires the use of thrust bearings to support the load.
Another important difference is in the versatility of helical gears.
While spur gears are limited to parallel shafts, helical gears can be used in various configurations, including crossed helical gears where the shafts are neither parallel nor intersecting, allowing for more complex machinery setups.
If you’re dealing with heavy-duty applications you might consider herringbone gears, a special type of double helical gear that eliminates the need for thrust bearings altogether by using opposing helical teeth to balance out the forces.
When to use Helical Gear
Helical gears are the way to go when smooth and quiet operation is key.
If your application involves high speed or requires a lot of power then a pair of helical gears is often the best solution.
The angled mating gear teeth engage gradually which reduces noise and vibration compared to straight-cut gears. This makes them ideal for noisy environments such as automotive transmissions or industrial machinery.
If you have multiple gears on the same gear shaft or parallel shafts then helical gears are preferred because they handle the load better, reducing wear and extending the life of the gear system.
How helical gears are manufactured
The manufacturing process of helical gears is a precise operation, designed to meet specific performance standards.
Helical gears are made using advanced methods such as hobbing, milling, or grinding where the gear teeth are cut at helix angles.
These angles are critical because they determine how the gear will engage with its counterpart and directly affect the gear’s performance. The gear teeth must be cut to extreme precision to maintain the correct angle and tooth profile to ensure smooth and quiet operation in noisy and vibration-sensitive applications.
After the initial cutting, the gears are often heat-treated to increase strength and durability and then ground to achieve the required surface finish and accuracy.
Types of Helical Gears
- Regular
- Double
- Herringbone
Standards
Helical gears are manufactured in a variety of standard sizes, which can differ based on the manufacturer and specific application requirements.
Read up on the standars to see which one you need for your projet.
Applications of Helical Gear
Helical gears are used in various industries because of their efficiency and ability to handle more load with quieter operation than spur gears.
Their versatility makes them suitable for applications where noise reduction and smooth power transmission are critical. You’ll find them in automotive transmissions and industrial machinery.
In some cases, helical gears are paired with herringbone gear for even more load capacity and balance.
They’re often used when the gear wheel needs to run at high speed or under heavy load.
Here are some common applications where helical gears are used:
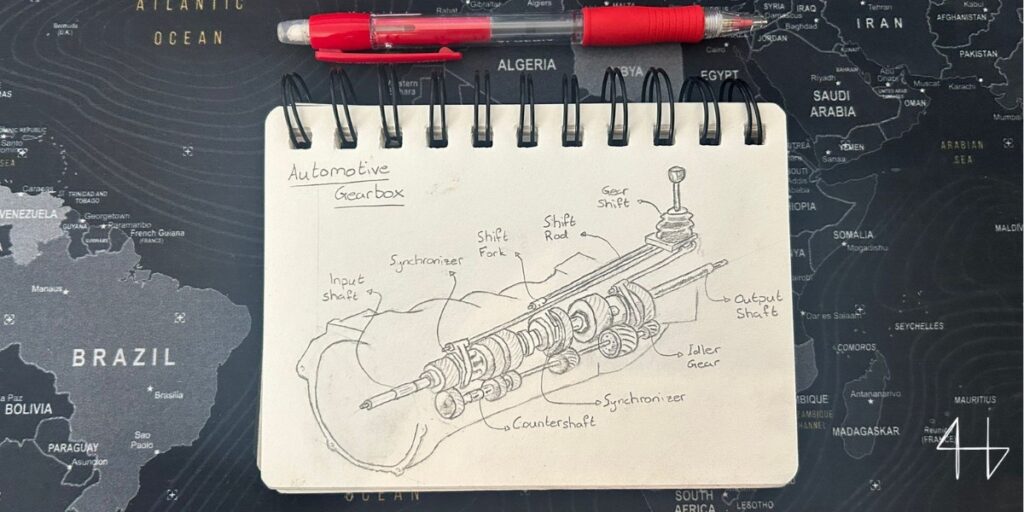
Automotive Transmissions
You’ll find helical gears in car transmissions, mostly in compounded gear trains inside gearboxes.
In m gearboxes, helical gears are critical because they can handle high speed and heavy load while keeping noise and vibration to a minimum.
You wouldn’t want to drive a loud car with jerky movements. That’s why the smooth transmission that you’ll get from helical gears is important.
Industrial Gearboxes
Helical gears create a reliable power transmission under heavy loads where you need high performance and precision.
Whether in conveyor systems, heavy machinery, or processing equipment helical gears ensure industrial gearboxes run smoothly and efficiently and extend the life of the gears and the equipment they drive.
Robotics
In robotics where precision and reliability are critical helical gears excel.
Robots need to be so precise that there isn’t really any other option besides helical gears with a very low tolerance.
Their smooth and controlled motion makes them perfect for driving robotic joints and mechanisms that require exact positioning.
Helical Gear Advantages and Disadvantages
Helical gears have many advantages but smooth operation comes with a cost.
Knowing these pros and cons can help you decide if the helical gear is really what you need or if a simple spur gear will do the trick.
Here’s a breakdown of their advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages
Disadvantages
Limitations
Now pay attention. These are the potential red flags you’ll need when considering adding helical gears to your design.
One major drawback is the generation of axial thrust forces due to the angled teeth which can require additional support and increase overall system complexity. Unlike cylindrical gears which don’t produce these forces, helical gears need specially designed bearings or housing to manage this thrust.
The spiral teeth stay in contact for longer which leads to an increase in heat generation. If your system is prone to overheating or is heat-sensitive, this could be a dealbreaker.
Additionally, you need to ensure that the same helix angle otherwise you can cause misalignment. This will increase wear and chances of failure. No bueno.
Conclusion
In summary, helical gears provide many benefits including smoother and quieter operation than spur gears making them perfect for applications that require precision and load distribution.
Their unique design with angled teeth and the same helix angle minimizes noise and vibration and enhances overall performance in systems like robotics and industrial machinery.
However, the generation of axial thrust forces and the need for additional support structures can complicate the design and increase cost.
By weighing these advantages against the limitations you can make an informed decision if helical gears are the right choice for you.
Knowing these will ensure your gear system runs smoothly and is tailored to your needs.
FAQs

Are helical gears efficient?
Yes, helical gears are very efficient.
Their design provides smoother and quieter operation than spur gears which means better performance and less energy loss during operation.
Are spur or helical gear stronger?
Helical gears are stronger than spur gears due to their angled teeth which distribute the load across multiple teeth at the same time.
This design reduces localized stress and allows helical gears to handle higher loads and torque making them more robust for high demand applications.
What is the main disadvantage of helical-cut gears?
The main disadvantage of helical cut gears is the generation of axial thrust forces.
Unlike straight-cut gears, helical gears produce axial loads due to their angled teeth.
This requires additional support like bearings or special housing which can increase complexity and cost.